本文共 2258 字,大约阅读时间需要 7 分钟。
好文推荐
作者:LKV_刘言
功能
用于为App提供初始化回调能力。体系化得将各种App内的功能模块、所引入的SDK的初始化联合起来,不各自为战。一方面能够将所有的初始化方式进行统一,在代码学习层面便于进入。另一方面,在初始化方式收敛后也能够有效的做性能数据监控。
配置
implementation "androidx.startup:startup-runtime:1.0.0"
使用
实现子类
每一个需要初始化的组件实现一个Initializer<T>的子类

并实现两个方法:
create这个方法要求返回你要初始化的组件的对象实例,可以new出来,也可以使用Builder等等,by your selfdependencies这个方法用来返回一系列的Initializer的子类的Class集合。意义是告知初始化框架,当前这个组件的初始化需要依赖其他的哪些组件初始化。可以没有有效内容。
实例(来自官方)
// Initializes WorkManager.class WorkManagerInitializer : Initializer{ override fun create(context: Context): WorkManager { val configuration = Configuration.Builder().build() WorkManager.initialize(context, configuration) return WorkManager.getInstance(context) } override fun dependencies(): List >> { // No dependencies on other libraries. return emptyList() }}
声明Manifest
两点注意:
- 要在Manifest中声明其原理中真正使用的ContentProvider类
androidx.startup.InitializationProvider,注意author要携带${applicationId}来避免与其他App产生冲突 - 记得一定要在这个provider下声明
meta-data
第一点不做解释了,其基本原理就是依靠ContentProvider的onCreate会在应用初始化时被自动调用这一点。
关于第二个需要解释:
Startup会去找自己Provider下声明的第一个meta-data所对应的类,来对他进行初始化,如果他声明了他有依赖项,那么他的依赖项也会被初始化。这样,一个初始化链路就行程了。
实例:
meta-data支持声明多个,只要他们的android:value都是androidx.startup就会被收集到:

原理
概览
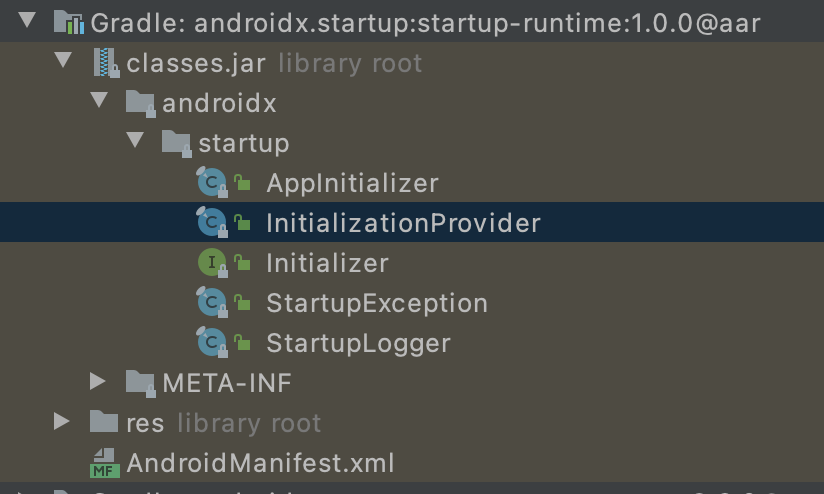
核心
ContentProvider的onCreate生命周期会在Application的onCreate之前被ActivityThread调用:
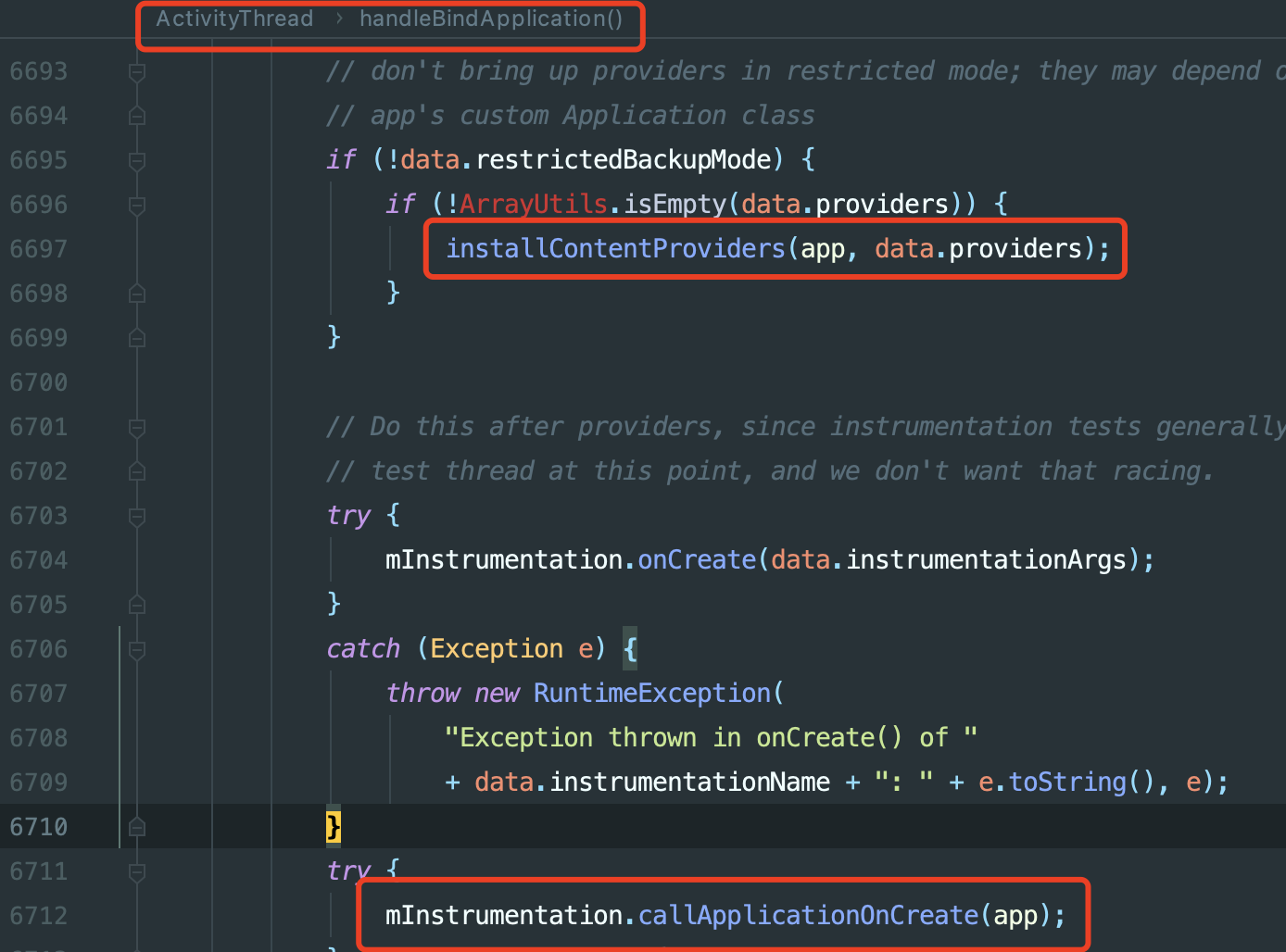
并且,这个行为是系统行为,不需要用户去主动触发,也就节省了XXX.init这种代码调用。
流程
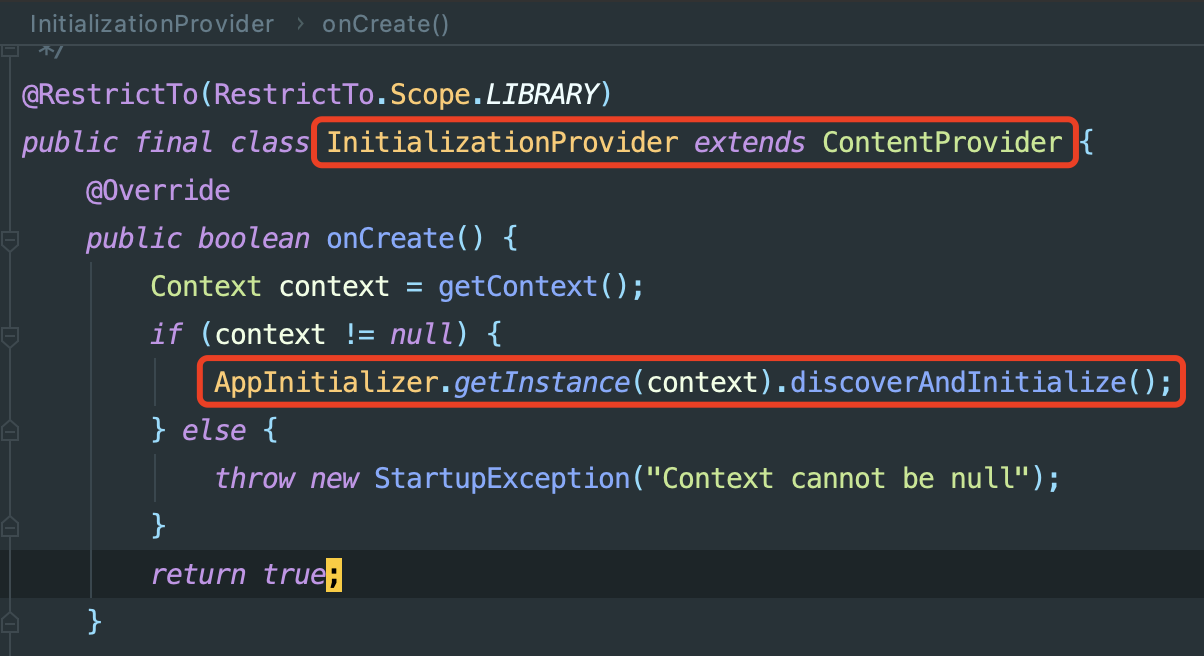
InitializationProvider调用AppInitializer.discoverAndInitialize()方法AppInitializer.discoverAndInitialize()扫描AndroidManifest.xml中InitializationProvider下的注册信息中的meta-data进行初始化组件发现:
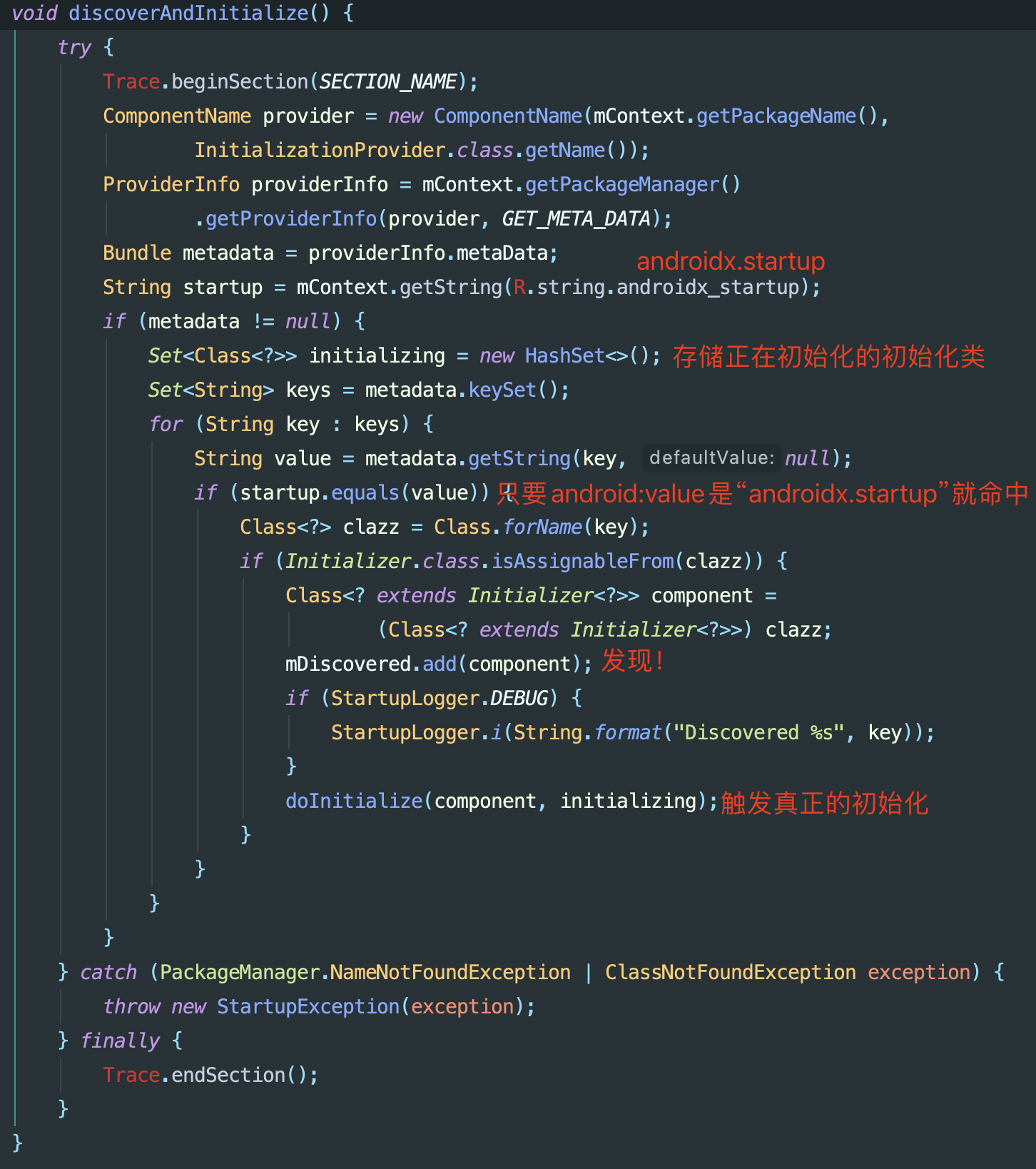
需要注意的是:
- 只要
meta-data的android:value是androidx.startup那么就可以被收集到,后续的触发是按照在Manifest中声明的顺序进行的 - 截图中代码没有提到的,会使用Map
mInitialized来确保每个类只会被初始化一次,而通过临时的initializing确保在依赖关系中不允许循环依赖
第二点可以在下一步得到验证:
- 调用
AppInitializer.doInitialize()
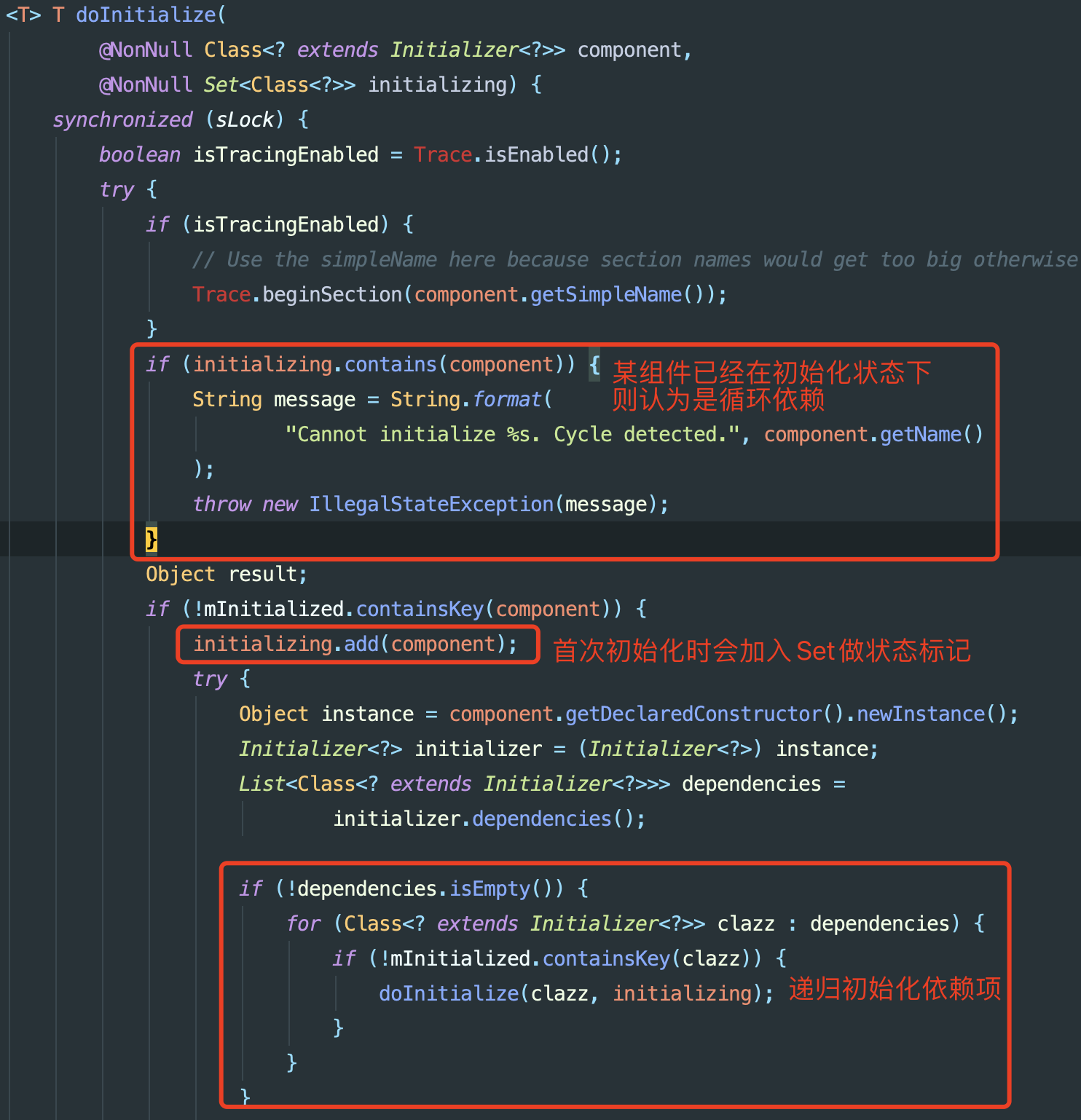
补充该方法的后续代码:
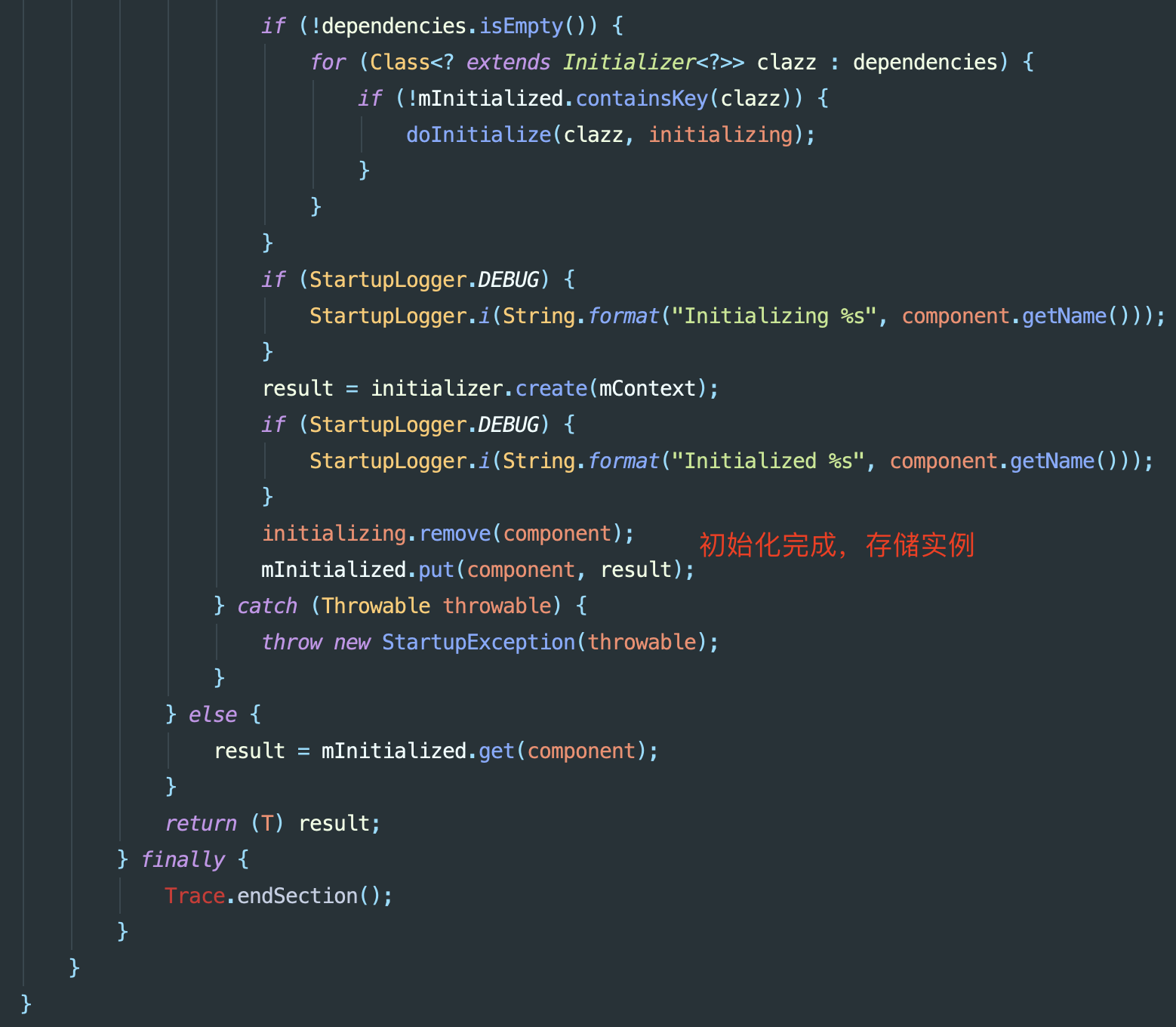
总结
- 初始化类应该具有
public的无参构造函数 - 初始化中的状态通过Set存储Class达成,初始化完成的状态由Map以Class为Key,对应
create所产生的对象为Value表达 - 不能有循环依赖
写在最后
Startup库无疑为开发者提供了最为便捷的初始化方式,并且还贴心的提供了初始化项按照依赖关系进行的功能。但笔者认为,其在成熟、多样的产品中,有几点不足:
- 不支持外部定制、监听相关初始化数据,如初始化时间的上报和超时报警
- 不支持延迟初始化、懒加载初始化等多样的初始化类型
- 与2类似,其初始化类型单一,或者说都可以认为是普通的初始化。如果想要在所有前边插入一个、所有后边插入一个作为特殊的初始化项,那么还需要开发者自行开发
一来,通过本文读者可以更明白该组件背后做了什么,可以更加自信、笃定、灵活的使用。另一方面,如果也认可笔者提到的问题的话,相信解法也是相对比较明确的,相信大家可以打造出适合自己的工具。
大家如果还想了解更多Android 相关的更多知识点,可以加入Android粉丝交流群:

转载地址:http://qrd.baihongyu.com/